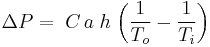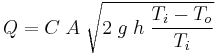Stack effect
Stack effect is the movement of air into and out of buildings, chimneys, flue gas stacks, or other containers, and is driven by buoyancy. Buoyancy occurs due to a difference in indoor-to-outdoor air density resulting from temperature and moisture differences. The result is either a positive or negative buoyancy force. The greater the thermal difference and the height of the structure, the greater the buoyancy force, and thus the stack effect. The stack effect is also referred to as the "chimney effect", and it helps drive natural ventilation and infiltration.
Contents |
Stack effect in buildings
Since buildings are not totally sealed (at the very minimum, there is always a ground level entrance), the stack effect will cause air infiltration. During the heating season, the warmer indoor air rises up through the building and escapes at the top either through open windows, ventilation openings, or other forms of leakage. The rising warm air reduces the pressure in the base of the building, drawing cold air in through either open doors, windows, or other openings and leakage. During the cooling season, the stack effect is reversed, but is typically weaker due to lower temperature differences.
In a modern high-rise building with a well-sealed envelope, the stack effect can create significant pressure differences that must be given design consideration and may need to be addressed with mechanical ventilation. Stairwells, shafts, elevators, and the like, tend to contribute to the stack effect, whereas interior partitions, floors, and fire separations can mitigate it. Especially in case of fire, the stack effect needs to be controlled to prevent the spread of smoke.
Stack effect in flue gas stacks and chimneys
The stack effect in industrial flue gas stacks is similar to that in buildings, except that it involves hot flue gases having large temperature differences with the ambient outside air. Furthermore, an industrial flue gas stack typically provides little obstruction for the flue gas along its length and is, in fact, normally optimized to enhance the stack effect to reduce fan energy requirements.
Large temperature differences between the outside air and the flue gases can create a strong stack effect in chimneys for buildings using a fireplace for heating. Fireplace chimneys can sometimes draw in more cold outside air than can be heated by the fireplace, resulting in a net heat loss.
The driving force for the stack effect
There is a pressure difference between the outside air and the air inside the building caused by the difference in temperature between the outside air and the inside air. That pressure difference ( ΔP ) is the driving force for the stack effect and it can be calculated with the equations presented below.[1][2] The equations apply only to buildings where air is both inside and outside the buildings. For buildings with one or two floors, h is the height of the building. For multi-floor, high-rise buildings, h is the distance from the openings at the neutral pressure level (NPL) of the building to either the topmost openings or the lowest openings. Reference[1] explains how the NPL affects the stack effect in high-rise buildings.
For flue gas stacks and chimneys, where air is on the outside and combustion flue gases are on the inside, the equations will only provide an approximation and h is the height of the flue gas stack or chimney.
-
where: ΔP = available pressure difference, in Pa C = 0.0342 a = atmospheric pressure, in Pa h = height or distance, in m To = absolute outside temperature, in K Ti = absolute inside temperature, in K
-
where: ΔP = available pressure difference, in psi C = 0.0188 a = atmospheric pressure, in psi h = height or distance, in ft To = absolute outside temperature, in °R Ti = absolute inside temperature, in °R
The flow induced by the stack effect
The draft or draught flow rate induced by the stack effect can be calculated with the equation presented below.[1][2][3] The equation applies only to buildings where air is both inside and outside the buildings. For buildings with one or two floors, h is the height of the building and A is the flow area of the openings. For multi-floor, high-rise buildings, A is the flow area of the openings and h is the distance from the openings at the neutral pressure level (NPL) of the building to either the topmost openings or the lowest openings. Reference[1] explains how the NPL affects the stack effect in high-rise buildings.
For flue gas stacks or chimneys, where air is on the outside and combustion flue gases are on the inside, the equation will only provide an approximation. Also, A is the cross-sectional flow area and h is the height of the flue gas stack or chimney.
-
where: Q = stack effect draft/draught flow rate, m³/s A = flow area, m² C = discharge coefficient (usually taken to be from 0.65 to 0.70) g = gravitational acceleration, 9.81 m/s² h = height or distance, m Ti = average inside temperature, K To = outside air temperature, K
-
where: Q = stack effect draft/draught flow rate, ft³/s A = area, ft² C = discharge coefficient (usually taken to be from 0.65 to 0.70) g = gravitational acceleration, 32.17 ft/s² h = height or distance, ft Ti = average inside temperature, °R To = outside air temperature, °R
Also, this equation is only valid when the resistance to the draft flow is caused by a single orifice characterized by the discharge coefficient C. In many, if not most situations, the resistance is primarily imposed by the flue stack itself. In these cases, the resistance is proportional to the stack height H. This causes a cancellation of the H in the above equation predicting Q to be invariant with respect to the flue height.
See also
References
- ^ a b c d Natural Ventilation Lecture 2
- ^ a b Natural Ventilation Lecture 3
- ^ Natural Ventilation, Andy Walker, National Renewable Energy Laboratory (US Department of Energy)